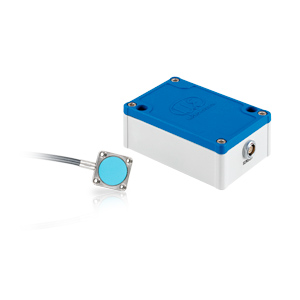
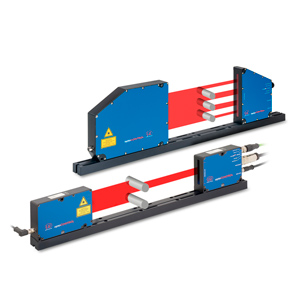
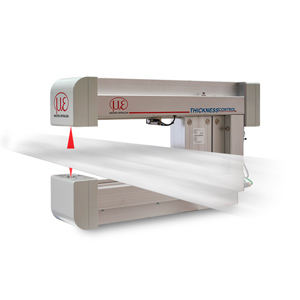
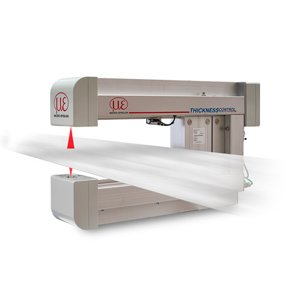
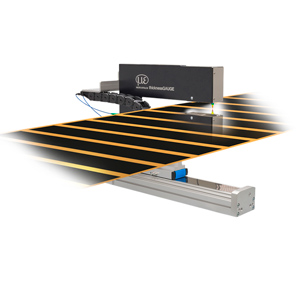
Lifting height, lifting
Lifting height is a factor which must be measured very frequently. A lifting height measurement is necessary everywhere where automatic lifting processes should make the daily work easier. The measurement system can be installed subsequently or already considered and integrated during the planning of the system.